Key points of all CBT therapies
Focuses on identifiable thought processes and definable behaviours
Focuses on here and now, in addition to past history
Interactions happen between the environment/context, thoughts, emotions, behaviours, and physiology.
Targets maladaptive behaviours and cognitions
Clear goals, collaborative, and short-term
Well-suited to empirical research
Thoughts are considered central to the regulation of behaviour
Thoughts, assumptions, and beliefs are seen as hypotheses, not facts
Beck’s CBT
Cognitive triad:
Negative thoughts about self, world, and future
Leads to depression
Cognitive distortions:
Overgeneralising - “I always mess up”
Catastrophising - Imagining the worst case scenario
Dichotomous thinking
Personalising
Labelling - “I’m a loser” vs “I made a mistake”
Selective abstraction - focusing on one negative detail rather than seeing the whole picture
Automatic thoughts, intermediate beliefs, core beliefs
Cognitive restructuring using Socratic dialogue
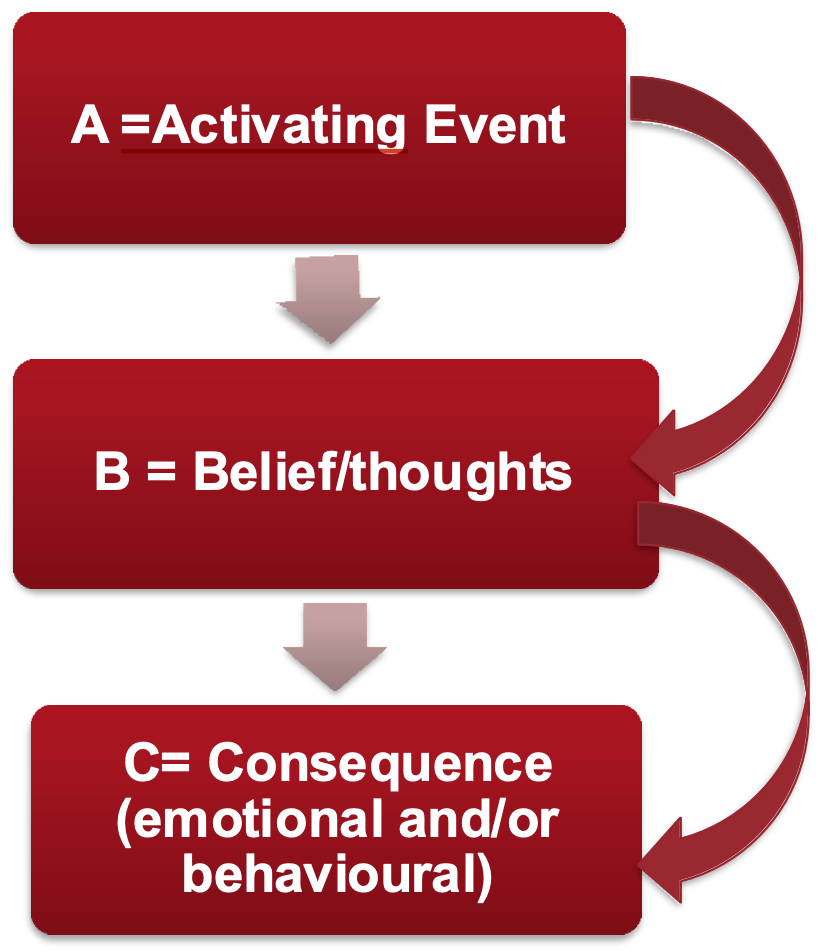
Albert Ellis’ ABC Model
Patterns of cognition can be seen within different types of disorders:
Anxiety – physical and/or social threat
Depression –loss or failure
Anger – hostile intent, or revenge
The behavioural perspective of CBT incorporates the application of learning to therapy.
This is seen in therapies such as exposure therapy & aversion therapy
First sessions:
Assessment/diagnosis/questionnaire to define the problem and set goals, through psychoeducation therapist explains nature and process of CBT, building rapport.
Middle Sessions:
Client is taught to identify, evaluate, and replace maladaptive automatic thoughts with more adaptive cognitions. This is rehearsed through self-monitoring and homework.
Behavioural strategies (exposure, relaxation, etc.) may support solidifying positive change. Homework is a key element (e.g., completion of various worksheets that the client will complete and bring along to the next session to discuss. Examples: thought record; wide variety of other worksheets and/or activities; etc.)
Final Sessions:
Solidify gains, focus on prevention of recurrence.