Observation skills
Observe the client and yourself throughout the conversation
Attending
Attend to what the person is saying, doing, the tone of their voice, and their body language
Attending is being with the person, both physically and psychologically
V V V B
Verbal Behaviour
Discrepancies
Key Words
Vocabulary of Emotions
Primary emotions are universal across all cultures
Social emotions are largely learn from family and culture and are related to our primary emotions. These emotions cannot be felt without the social context
Visual - Use the appropriate amount of eye contact for the culture / gender difference.
Vocal - Use warmth and variation of your vocal tone in order to convey interest
Verbal - Staying on topic and using paraphrases or five questions shows that you are paying attention
Body Language - Face the client, lean slightly forward, and have an expressive face and gestures.
Active Listening
Definition: A communication process that requires intentional participation, decision making, and responding.
Active listening is hearing what the person is NOT saying directly with their words.
Active listening conveys to the person that they have been fully heard by using skills such as:
Encouraging
Paraphrasing
Summarising
Tips for active listening:
Pay attention internally and externally
Know when to ask for more details and want to stay quiet
Pay attention to the person’s, intonation and emotions when speaking
Listen for adjectives and ask for elaboration
Ask for clarification on “you know what I mean”
Attention to non-verbal cues
Be comfortable with allowing silence
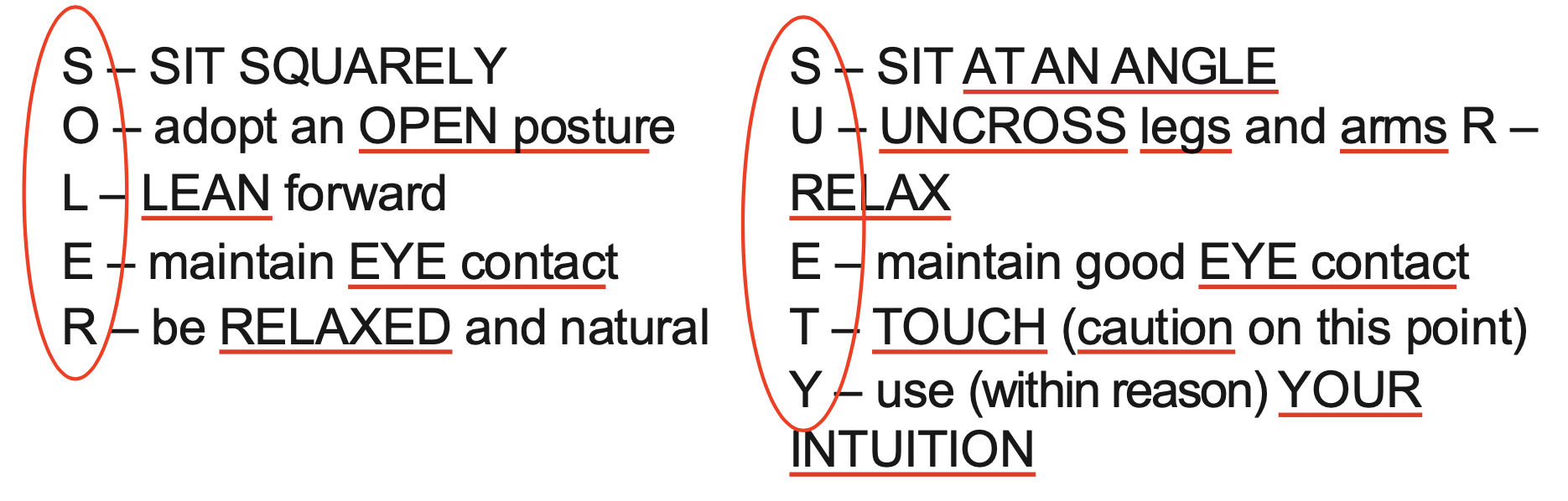
Non-Verbal Behaviour
Observe:
Eye contact patterns
Body Language
Vocal qualities
Shifts and changes may indicate discomfort or other emotions. For example, looking downwards, fidgeting, playing with jewellery, talking, more/less, etc.
Observe:
Verbal tracking (staying with the story)
Pay attention to and make a note of discrepancies between:
Non-verbal behaviours
Two statements
Words and actions
Incompatible goals
People
The client and a situation
Be careful about pointing out discrepancies. It may be best to simply reflect discrepancies in a narrative in order to help explore the issue.
Notice, keywords that are repeated
Use keywords in feedback to clarify a theme
Keywords may help to clarify, meaning, identify patterns, or improve record for future sessions
Layers of emotion:
People may express a single emotion, but it is common for this to be combined with other emotion and below the surface.
Example: Melanie laughs off a Fail grade on an assessment but blames the tutor. Melanie may be actually feeling sad, paired with anger and guilt.
Human development is rooted in emotional experience.
Reflecting emotions may lead client in new directions with new discoveries.
Encouragers
Head notes and positive facial expressions
Minimal verbals (uh-huh)
Repeat keywords from the last statement
Silence when appropriate
Barriers to Active, Listening
Distraction
Emotional barriers
Expressing judgement
Prejudices, biases, assumptions, labelling
Fatigue
Language barriers