What is mindfulness?
Mindfulness has two aspects:
Present moment awareness, attention or focus
Lack of judgment or reactivity
Can be spontaneous (unintentional) or deliberate (intentional)
Trait-like mindfulness is a disposition
State-like mindfulness is a practice
Mindfulness brings clarity through the separation of an event from the judgment and emotions that follow
State Mindfulness uses the focus on our current state in order to develop mindfulness as a trait
Developing Trait Mindfulness
Engaging in regular mindful practice helps cultivate a mindful disposition
Mindfulness uses Neuroplasticity to strengthen brain regions associated with attention, emotional regulation, and self-awareness
The more you practice mindfulness, the more it becomes an enduring part of your character
Mindfulness interventions lasting from 2 to 12 weeks, have been shown to provide a benefit
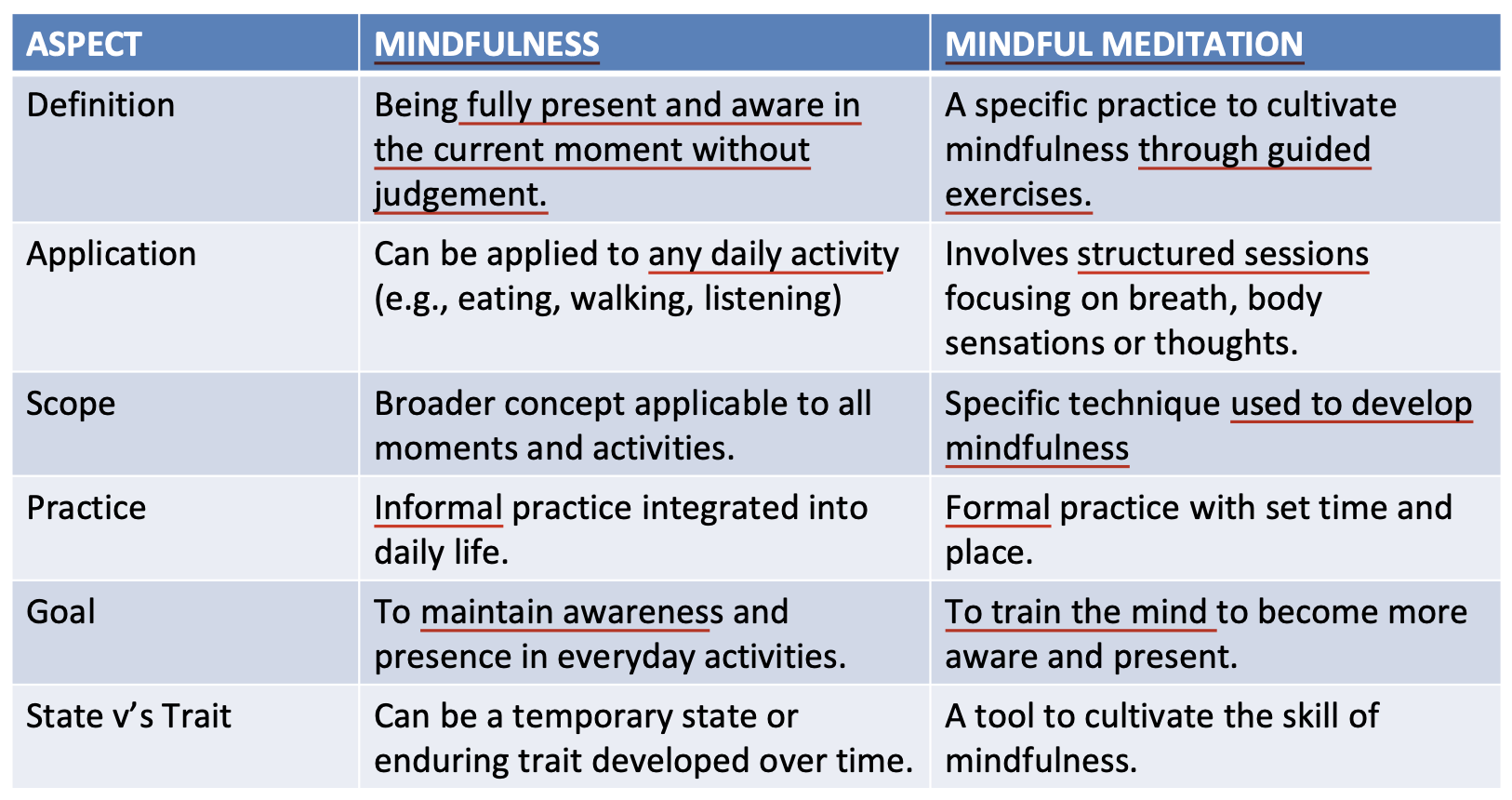
Mindfulness vs Mindful Meditation
Mindfulness Interventions
Interventions have been shown to be useful for:
Physical health – chronic pain, immune response, positive health-related behaviours
Mental health – depression, anxiety, PTSD
Cognition – attention, working, memory, meta-cognition
Affect/mood – negative emotions, positive emotions, rumination
Interventions have been used with some success in schools