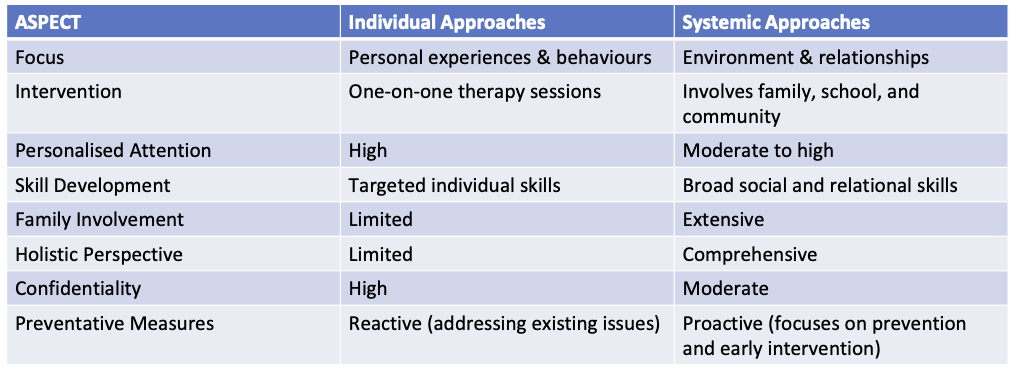
Case Study for Individual vs Ecological Approaches
Individual Approaches:
Focus on the person:
Mainly considered the persons, thoughts, emotions and behaviours. E.g. CBT therapy.
Personal responsibility:
Responsibility for mental health is placed on the individual
Internal factors:
Individual approaches, primarily, consider internal factors, such as genetics, personality, traits, and personal experiences
Interventions:
Interventions are typically one on one to the individuals specific needs
Individual interventions:
Purchase such as CBT, maybe effective for young people in some situations
Systemic interventions:
This shows that interventions are more affective for child, focus problems such as conflict issues, emotional problems, and recovery from abuse.
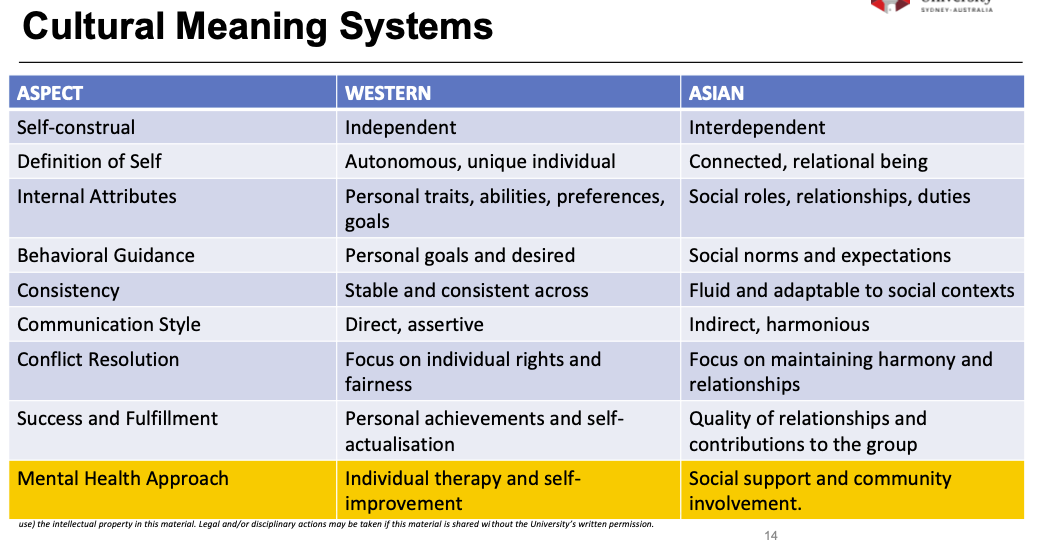
The Role of Culture in Individual & Systemic Therapy
Cultural norms and family dynamics:
In western cultures emphasise individual autonomy. Interventions may focus on improving communication and relationships within the family unit.
In non-western cultures, systemic approaches are often more congruent. Family and community involvement in therapy enhances effectiveness.
Community support:
Western cultures still focus predominantly on individual responsibility for mental health.
Non-Western cultures more naturally integrate community and social support.
Autonomy:
Personal control serves as a protective factor in western cultures
Western cultures tend to define a person by their personal characteristics, whereas non-western cultures tend to define a person as being interdependent within their social roles, realtionships and duties.
Limitations of Individual Approaches:
Often ignores external factors
Overemphasis on personal responsibility
Only utilises one-on-one treatments, instead of involving family and community.
Access to individual therapy is often limited and inequitable
Short-term focus on symptom relief over addressing underlying issues
Emphasising individual responsibility contributes to stigma and self-blame
Focuses on treatment, rather than prevention by addressing systemic factors
Systemic Approaches:
Focus on the person’s environment
Consider interactions between systems and the individual
Consider external factors such as social support & cultural norms
Include community, family, and policy as interventions
Ecological systems research can be used to inform policy development